- Published on
AWS Route53 Cheat Sheet - Complete DNS Service 2025
- Authors

- Name
- QuizCld
A DNS (Domain Name System) server is like a phone book which translates human-friendly domain names like google.com into IP addresses for example 142.240.196.23 that computers use to communicate with each other.
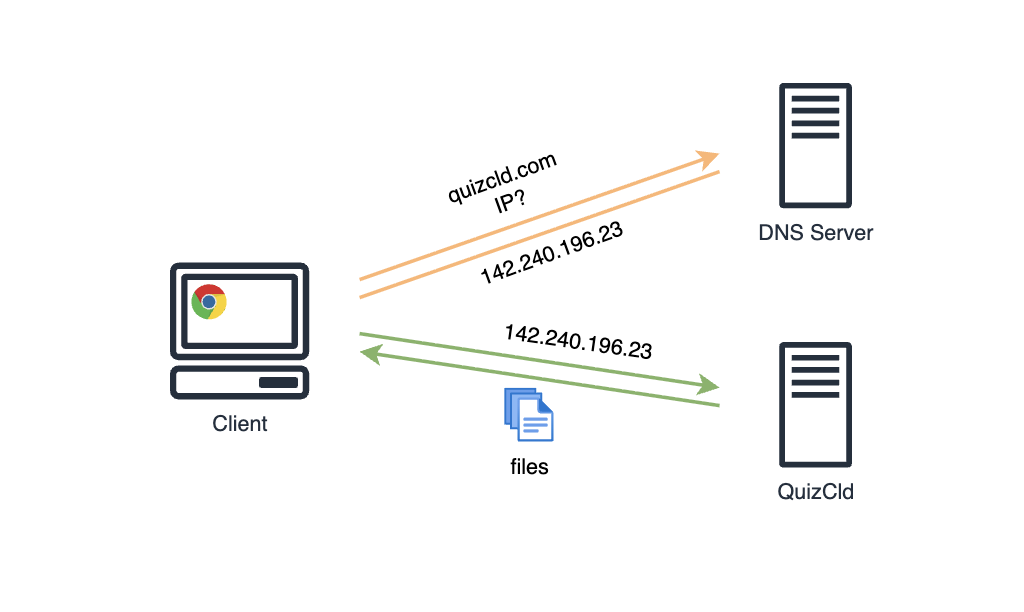
What is Amazon route53?
Amazon Route 53 is a highly available and scalable Domain Name System (DNS) web service. The table below is a summary about Amazon Route53 features.
Amazon route53 features?
Amazon Route53 provide three main features: domain registration, DNS routing, and health checking. Additionally, the service also providers the following features:
- Route 53 Resolver
- Amazon Route 53 Resolver on Outposts
- Route 53 Resolver DNS Firewall
- Traffic Flow
- Amazon Route 53 Profiles
Amazon Route53 domain registrator
If you create a website or application, and deploy it in virtual machine for example EC2, users from internet can access to the domain using the public IP addresss. However, to easier to remember, your application need a name known as domain name such as quizcld.com. Similar to Godaddy or Namecheap, the Amazon Route53 also provide the feature, you can follow the steps to register a domain:
- Choose a domain name and check availability.
- Register with Route 53 by providing ownership and contact details. Route 53 will setup automatically for you by creating hosted zone and add nameserver to the domain.
- Amazon will send your information to the registrar for the domain (Amazon Registrar, Inc. or thier registrar associate, Gandi.)
- Registrar sends your information to the registry for the domain
- The registry stores the information about your domain in their own database and also stores some of the information in the public WHOIS database.
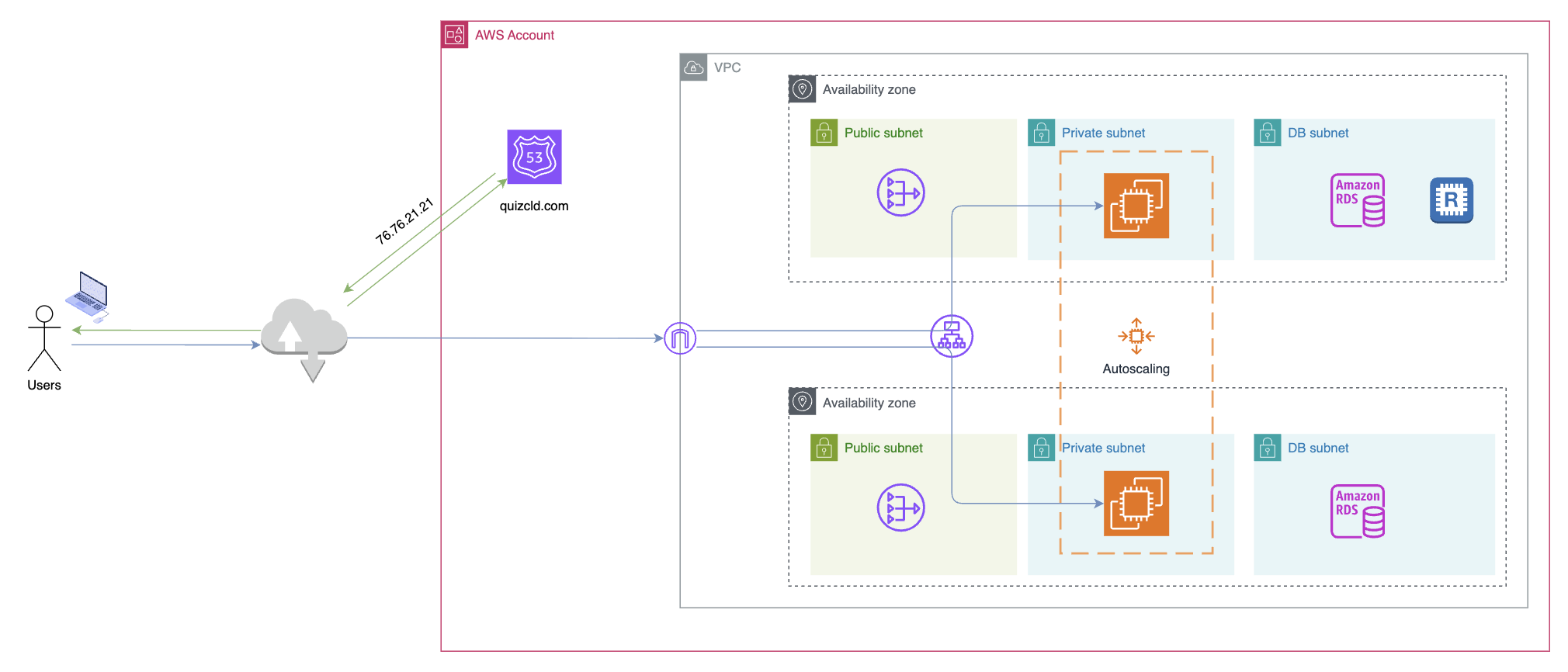
Amazon Route53 DNS routing
When Route 53 is your DNS service, it routes internet traffic to your website by translating friendly domain names like www.quizcld.com into numeric IP addresses, like 192.0.2.1, that computers use to connect to each other.
There are two steps to configure route traffic to your web application:
- Create a hosted zone. You can create either a public hosted zone or a private hosted zone
- Create records in the hosted zone. The records are where you want to route traffic for each domain name or subdomain name. For example, to create
www.quizcld.comdomain, you will create a recordwww.quizcld.comwith value is your server IP inquizcld.comdomain.
Amazon Route53 health checks
Amazon Route 53 health checks monitor the health and performance of your web applications, web servers, and other resources. There are four type of health checks:
- Health checks that monitor an endpoint: Route 53 health checks regularly test specified endpoints to ensure they are reachable, available, and functioning, optionally simulating real user requests.
- Health checks that monitor other health checks (calculated health checks): Route 53 can monitor the status of multiple health checks and notify you only when the number of healthy resources, like web servers, falls below a set threshold.
- Health checks that monitor CloudWatch alarms: Route 53 health checks can track CloudWatch alarms but only support standard metrics, basic stats, and alarms in the same AWS account.
- Amazon Application Recovery Controller (ARC) routing controller: health checks link to routing controls (on/off switches) that work with failover DNS records, letting you reroute traffic across Availability Zones or Regions.
Amazon Route53 use cases?
Scanario 1: Website hosting with custom domain
A learning platform wants to host their website on Amazon S3 and CloudFront and use a custom domain (e.g., blog.quizcld.com).
How Amazon Route53 helps:
- The company registers its domain quizcld.com through Godaddy, and using Route53 as a hosted zone.
- Route 53 manages the DNS records (A/AAAA, CNAME, MX, etc.) for the domain.
- It maps the domain name (blog.quizcld.com) to the CloudFront distribution or S3 static website endpoint.
Benefits: Users can access the website with a branded domain name, and Route 53 ensures high availability and low-latency DNS resolution. Additionally, the user cal also manage cloud resources via IaC (infrastructure as code) terraform for example.
Scanario 2: Latency-Based Routing for Global Users
A SaaS company has application servers running in US-East (Virginia) and Asia Pacific (Singapore). They want users to connect to the nearest server for better performance.
How Route 53 helps:
- The company sets up two DNS records with a Latency-based Routing Policy in Route 53.
- When a user in Asia queries the domain, Route 53 directs them to the Singapore server.
- When a user in the US queries, Route 53 routes them to the Virginia server.
Benefits: End users always connect to the lowest-latency endpoint, improving app responsiveness and user experience.
Scanario 3: Hybrid Cloud with On-Premises and AWS An enterprise runs a learning platform in its on-premises data center. To reduce costs and leverage AWS services, they begin migrating workloads to AWS. During migration, a service in AWS (inside a VPC) needs to call an internal service (internal.quizcld.com) that is still hosted on-premises. The domain is managed by the on-premises DNS server, and connectivity is established using AWS Direct Connect.
How Route 53 helps:
- The company sets up a Route 53 Resolver outbound endpoint in the VPC.
- They configure a forwarding rule so DNS queries for internal.quizcld.com are automatically forwarded to the on-premises DNS server via Direct Connect.
Benefits:
- Ensures seamless name resolution between AWS and on-premises environments.
- Enables hybrid workloads to communicate securely over Direct Connect without changing applications.
- Provides a scalable, managed DNS solution that simplifies migration and future cloud adoption.
Amazon Route53 best practice?
Follow recommendations for optimizing Amazon Route 53 health checks to ensure reliable monitoring of your resources DNS best practices:
- Understand the trade-offs between time to live (TTL) values and responsiveness versus reliability.
- Use alias records instead of CNAME records when possible for improved performance and cost savings.
- Configure default routing policies to ensure all clients receive a response.
- Leverage latency-based routing for minimizing application latency and geolocation/geoproximity routing for stability and predictability.
- Verify change propagation using the GetChange API for automated workflows.
- Delegate subdomains from the parent zone for consistent routing.
- Avoid large single responses by using multivalue answer routing.
Resolver best practices:
- Prevent routing loops by avoiding associating the same VPC with both a Resolver rule and its inbound endpoint.
- Implement security group rules to reduce connection tracking overhead and maximize query throughput.
- Configure inbound endpoints with IP addresses in multiple Availability Zones for redundancy.
- Be aware of potential DNS zone walking attacks and contact AWS Support if your endpoints experience throttling.
Amazon route53 pricing
With Amazon Route 53, you don't have to pay any upfront fees or commit to the number of queries the service answers for your domain. There are no contracts or minimum commitments for using Amazon Route 53. You pay only for the hosted zones that you configure and the number of DNS queries that Route 53 answers.
Hosted Zones & Records
A hosted zone is charged at the time it is created and on the first day of each subsequent month.
- $0.50 per hosted zone per month for the first 25 hosted zones
- $0.10 per hosted zone per month for additional hosted zones
| Item | Price | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| First 25 hosted zones | $0.50/zone/month | Not prorated |
| Additional hosted zones (26+) | $0.10/zone/month | Not prorated |
| Records per zone | Included up to 10,000 | - |
| Additional records (10,000+) | $0.0015/record/month | - |
| Testing grace period | Free if deleted within 12 hours | Queries still charged |
DNS Queries (Standard AWS Regions)
| Query Type | First 1B Queries/Month | Over 1B Queries/Month |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Queries | $0.40/million | $0.20/million |
| Latency-Based Routing | $0.60/million | $0.30/million |
| Geolocation/Geoproximity | $0.70/million | $0.35/million |
| IP-Based Routing | $0.80/million | $0.40/million |
| Alias to AWS Services | FREE | FREE |
| Private Hosted Zones | FREE | FREE |
Alias A/AAAA records that are mapped to the following AWS services do not incur a charge: Elastic Load Balancers, Amazon CloudFront distributions, AWS Elastic Beanstalk environments, Amazon API Gateways, Amazon VPC endpoints, Amazon S3 buckets that are configured as website endpoints, Amazon AppRunner, Amazon AppSync, Amazon OpenSearch, Amazon LightSail, and Amazon Global Accelerator.
Health Checks
| Type | AWS Endpoints | Non-AWS Endpoints |
|---|---|---|
| First 50 AWS endpoint checks | FREE | N/A |
| Basic health checks | $0.50/month | $0.75/month |
| Optional features (HTTPS, string matching, fast interval) | +$1.00/feature/month | +$2.00/feature/month |
Note: Health checks for ELB and S3 website endpoints are automatically free
Traffic Flow
| Feature | Price |
|---|---|
| Policy record | $50.00/record/month |
Only charged when policy is associated with a domain name
Resolver (Hybrid DNS)
| Component | Price |
|---|---|
| Resolver endpoint (ENI) | $0.125/ENI/hour |
| Queries through endpoints | 0.40/million (first 1B) and $0.20/million (over 1B) |
Minimum 2 ENIs required per endpoint
Resolver DNS Firewall
| Feature | Price |
|---|---|
| DNS queries inspected | 0.60/million (first 1B) and $0.40/million (over 1B) |
| Domain names stored | $0.0005/domain/month |
| Firewall Advanced rules | $0.16/hour per rule group per VPC |
| Managed domain lists | Included (queries charged) |
Route 53 Profiles
| Tier | Price |
|---|---|
| First 100 Profile-VPC associations | $0.75/hour per account per region |
| Additional associations (100+) | +$0.0014/association/hour |
Domain Registration
| Item | Price |
|---|---|
| Domain registration | Varies by TLD (view full list) |
| Default limit | 20 domains per account |
Promotional credits cannot be used for domain registration
Additional Features
| Feature | Price | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| DNSSEC signing | FREE | KMS charges apply for key storage |
| DNSSEC validation | FREE | - |
| Query logs | FREE | CloudWatch/S3/Kinesis charges apply |
Amazon Route53 cost example
Small Website (1 domain, 10M queries/month):
- Hosted zone: $0.50
- Queries: 0.40 per million)
- Total: ~$4.50/month
Using Alias to ELB (1 domain, 10M queries/month):
- Hosted zone: $0.50
- Queries: $0.00 (Alias queries free)
- Total: ~$0.50/month
Medium Site with Health Check (3 domains, 100M queries/month):
- Hosted zones: 0.50)
- Queries: 0.40/million)
- Health check: FREE (first 50 AWS endpoints)
- Total: ~$41.50/month
Conclusion
Amazon Route 53 stands as a comprehensive, enterprise-grade DNS service that seamlessly integrates with AWS infrastructure while maintaining compatibility with hybrid and multi-cloud environments. Its pay-as-you-go pricing model, starting as low as $0.50 per month for a hosted zone, makes it accessible for projects of any size—from personal blogs to global enterprise applications.
Key benefits:
- Versatility: Route 53 goes beyond basic DNS by offering domain registration, advanced routing policies, health checks, and hybrid DNS resolution through Route 53 Resolver.
- Cost efficiency: Leverage alias records for AWS services to eliminate query charges entirely. For most small to medium websites, monthly costs remain under $5.
- Global performance: With latency-based and geolocation routing, you can deliver optimal user experiences worldwide by directing traffic to the nearest or most appropriate endpoints.
- High availability: Built on AWS's proven infrastructure, Route 53 guarantees 100% availability SLA, ensuring your DNS queries are always answered reliably.
- Hybrid cloud ready: Route 53 Resolver bridges on-premises and cloud environments, making it an ideal choice for enterprises in cloud migration or running hybrid architectures.
Start Amazon Route53 practice exam for FREE